The configuration of the FNM Manager web panel follows a similar logic to FastNetMon. Below are the essential steps to perform a basic configuration.
1. Enable Traffic Capture
FNM Manager supports various telemetry protocols for traffic capture, including:
-
NetFlow (v5, v9, IPFIX).
-
sFlow.
-
Port Mirroring (if the above protocols are not compatible).
Steps:
-
Go to Settings > General.
-
Enable the desired protocols and configure the corresponding ports.
-
Adjust the sampling ratio if a value different from the default is used.
Important:
-
Configure the active and inactive flow timeout on your network devices (recommended: 30 seconds).
-
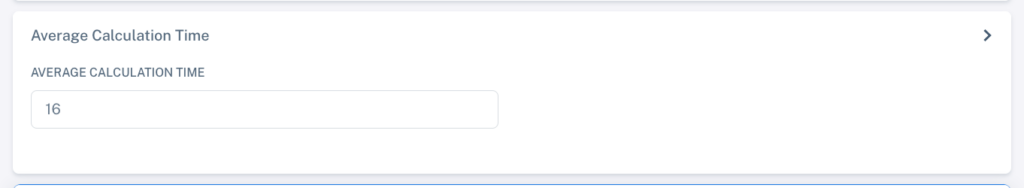
Adjust the Average Calculation Time in FNM Manager to be slightly higher than the timeout configured on the devices.
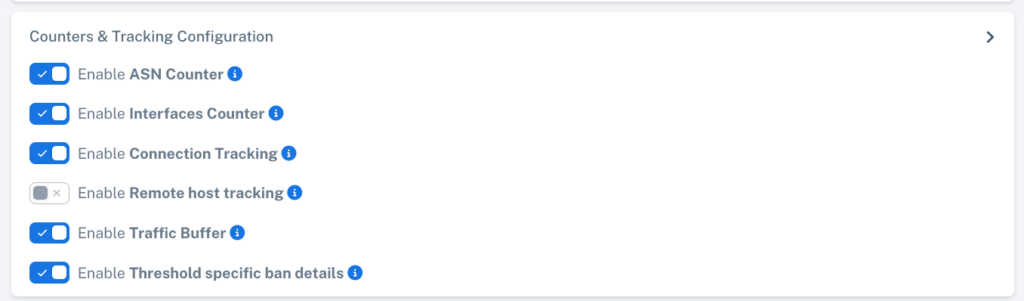
2. Enable Counters & Tracking
You can enable the counters and tracking options you want to analyze. Keep in mind that activating more options may increase hardware resource usage.
Available Options:
-
ASN Counters: Enable/disable traffic counting by ASN.
-
Interfaces Counter: Monitor traffic by interface.
-
Connection Tracking: Enable tracking of active connections.
-
Remote Host Tracking: Track remote IPs (not recommended for large environments).
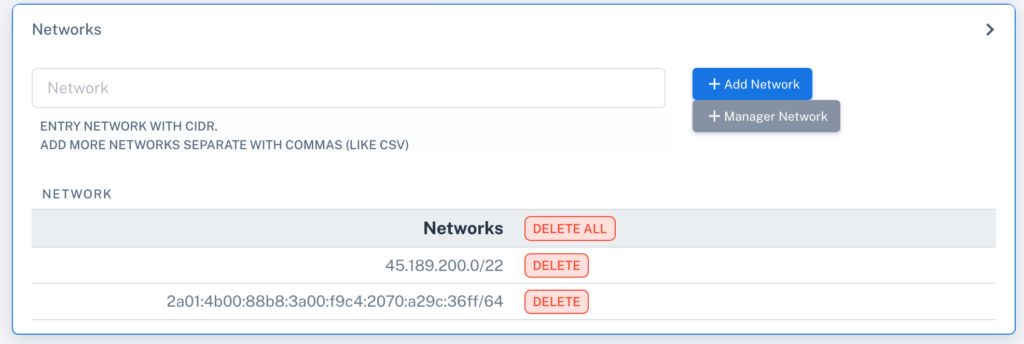
3. Configure Networks
You must define the networks that will be analyzed by FastNetMon. If a network is not configured here:
-
Its traffic will not be protected.
-
It will appear as "Others Traffic."
Configuration Options:
-
Add networks manually in CIDR format.
-
For large volumes of networks, you can associate an ASN, and FNM Manager will automatically detect the related networks.
Note: Keep the networks updated to ensure continuous protection.
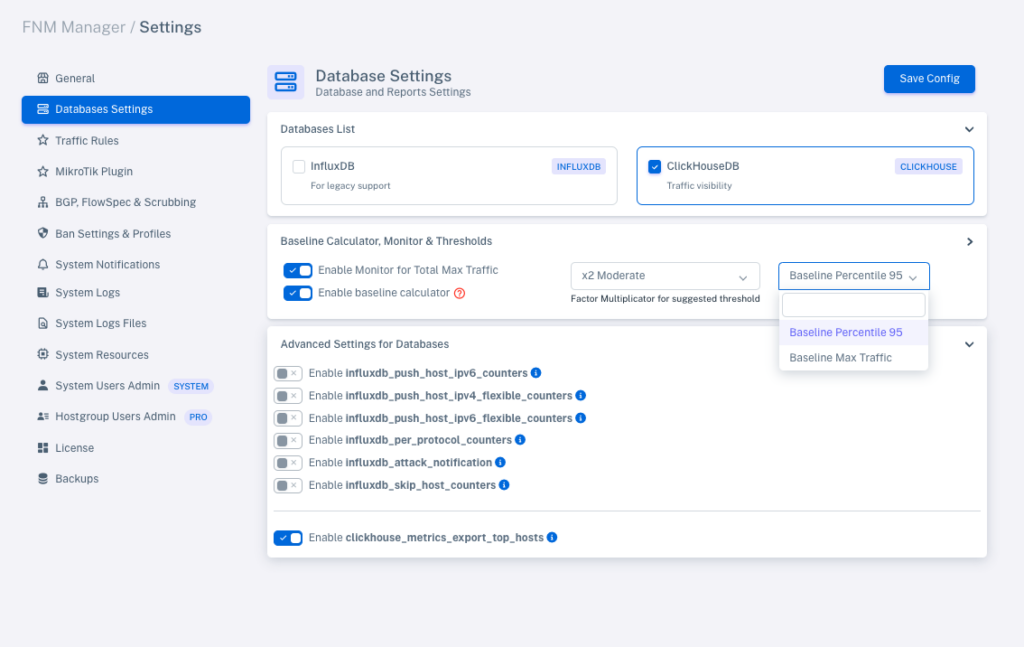
4. Configure Databases
FNM Manager requires ClickHouse as a mandatory database for its operation. You can also enable InfluxDB for legacy support purposes.
Additional Features:
-
Threshold calculator based on stored traffic.
-
Calculation by maximums or 95th percentile for each hostgroup.
5. Configure Customers / Hostgroups
By default, FastNetMon applies the same thresholds to all hosts in the network using the global hostgroup. However, you can create different hostgroups with customized thresholds to suit your needs.
Common Use Cases:
-
Enterprise customers.
-
ISP clients.
-
Content caches.
-
NAT or CGNAT groups.
Note: Hostgroups allow for more granular and specific configuration for each network segment.
Hostgroup/Customer Configuration:
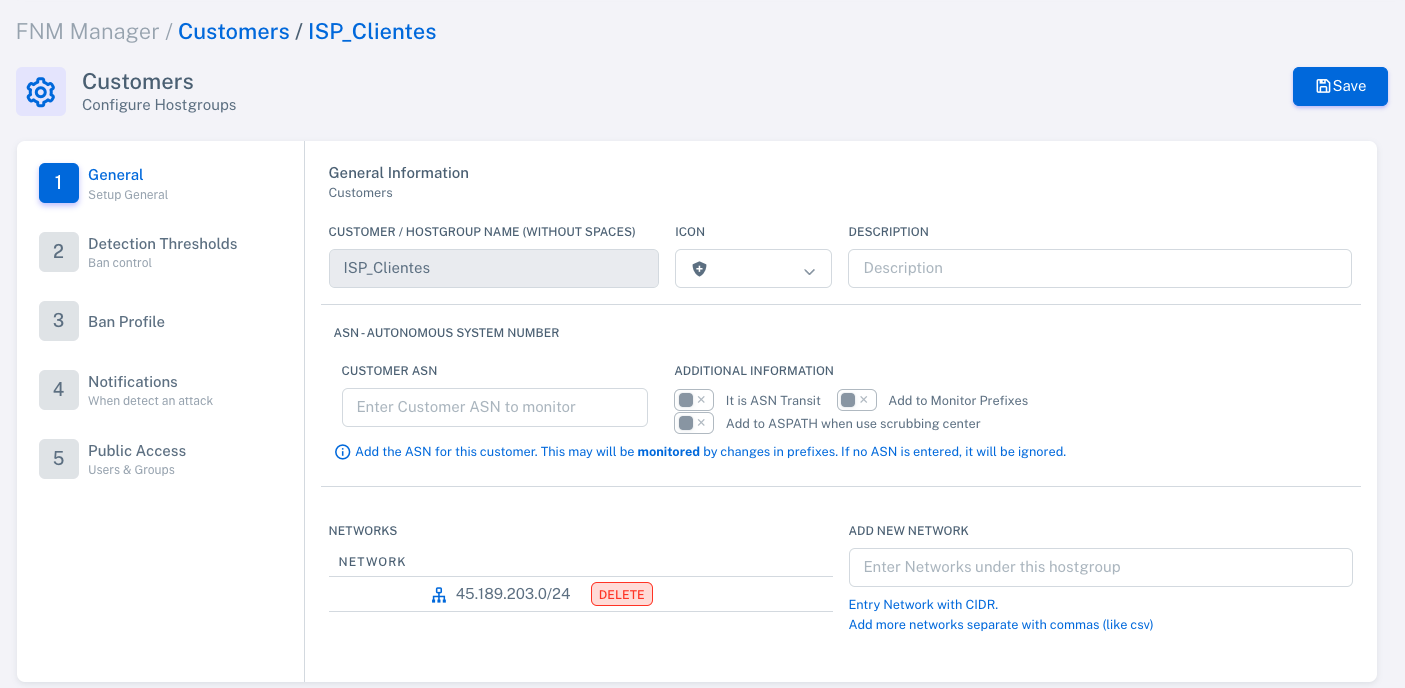
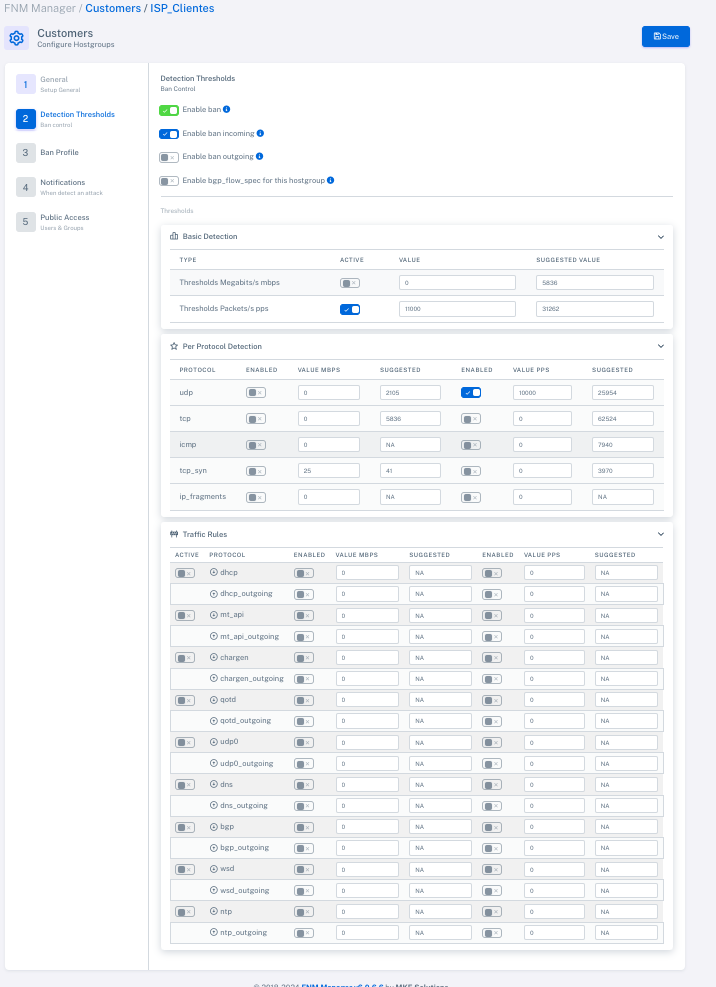
![]() Define thresholds for each group.
Define thresholds for each group.
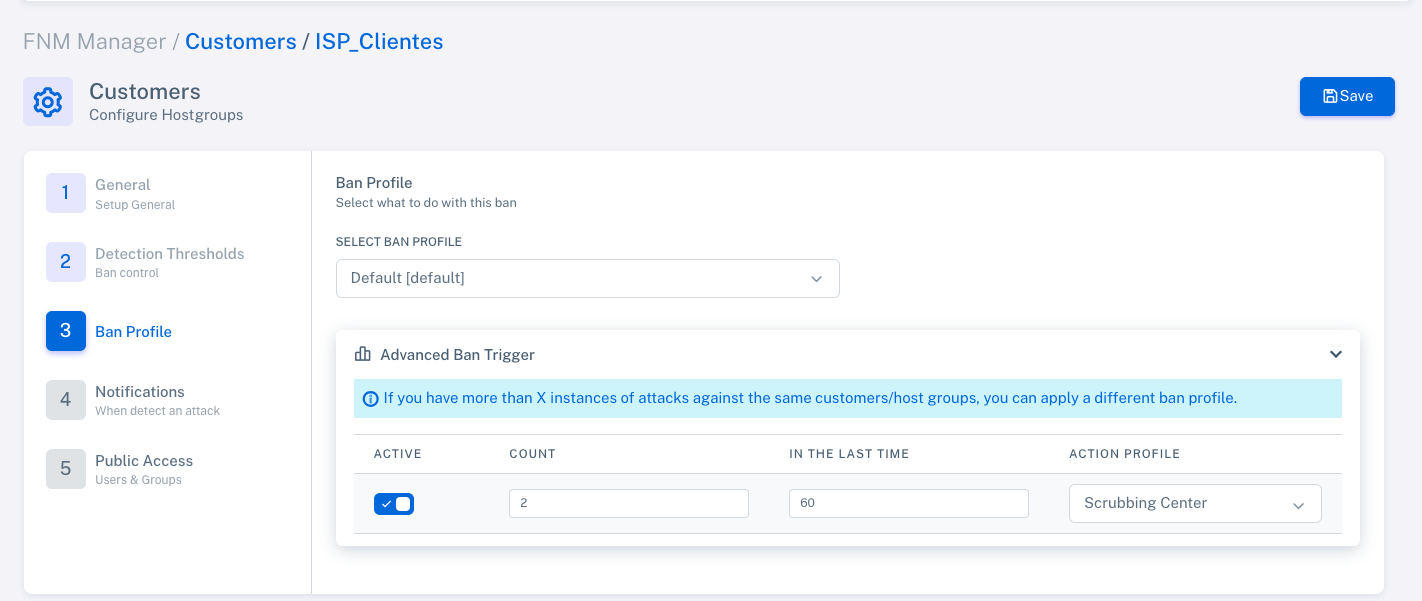
Configure banning actions or profiles.
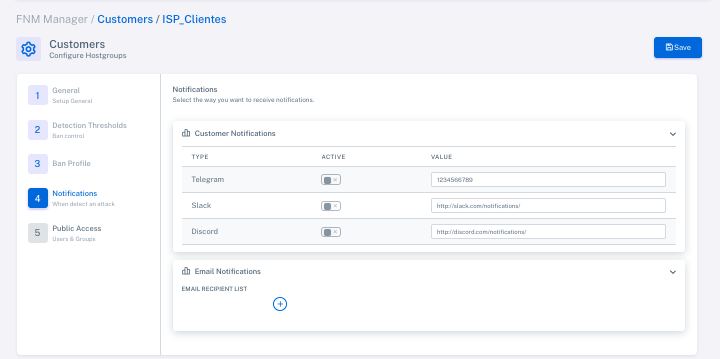
Set up notifications for the customer/hostgroup.
6. Configure Actions to Detect an Attack
Once thresholds are configured, activate the ban mode and define actions to mitigate an attack. Options include:
-
Blackhole: Publish a /32 via BGP with a specific community for routing policy handling.
-
Scrubbing Center: Publish a /24 via BGP to redirect traffic to a cleaning center.
-
FlowSpec: Create advanced filtering rules distributed via BGP.
-
MikroTik API: Send the /32 IP to a MikroTik device to add it to an address list and apply actions, such as NAT or masquerade.